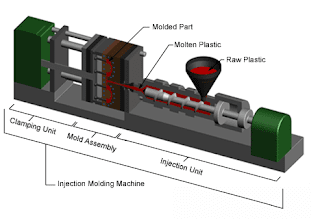
Injection molding is the most commonly used manufacturing process for plastic parts. The use of injection molding varies greatly in size, complexity, and application. It requires the use of injection molding machines, plastic materials and molds. The plastic is melted in an injection molding machine and then injected into the mold cavity, where it cools and solidifies into the final part.
Injection molding is used to produce thin-walled plastic parts for various applications, the most common of which is a plastic housing. The plastic shell is a thin-walled shell, usually requiring many rib-shaped frames and protrusions inside. These housings are used in a variety of products, including household appliances, consumer electronics, power tools, and car dashboards, etc. Other common thin-walled products include different types of open containers, such as boxes and containers. Injection molding is also used to produce several everyday items, such as toothbrushes or small plastic toys. Many medical devices like valves and syringes, are also manufactured using injection molding.
6 major advantages of injection molding:
1. Ability to form complex shapes and details
Basically, customers can achieve whatever custom shapes/ forms they like. Other types of manufacturing may have difficulties, if possible, in doing so. Take cardboard boxes for example, make shaped cardboard boxes requires handwork, at rather dear cost. Even so, no all shapes can be realized in cardboard boxes.
2. Excellent surface finish
First, plastic material has greater plasticity in property compared to most other materials. Secondly, the surface finish is determined by the molds. So once the mold is set up as required, the desired surface finish is acquired upon injected. And absolutely all the same, as they are out of one mold.
3. Good dimensional accuracy
If you need absolutely accurate dimensions, then injection molding is no doubt the number one choice. The trick is with the mold design and construction. So strong molding capability is required. Good dimensional accuracy is guaranteed by precision molds.
4. High productivity
Once the molds are ready, all the work becomes repetitive injection process of machines. High efficiency, no break (except for necessary mold maintenance regularly).
5. Low labor cost
Labor is almost the biggest cost of all projects. Plastic injection molding involves little labor, especially for manufacturers with robotic manipulators in place. Once the initial fixed investment is made, the more you produce, the less breakdown cost will be.
6. Waste materials can be recycled
No waste! As waste materials will be easily recycled for future injection.
Of course, everything has two sides. It's not all advantages only. The manufacture process of injection molding has its disadvantages as follows. What suits you is the best.
Disadvantages of injection molding:
1. Limited to thin-walled parts
2. High tool and equipment cost
3. Very long delivery time possible